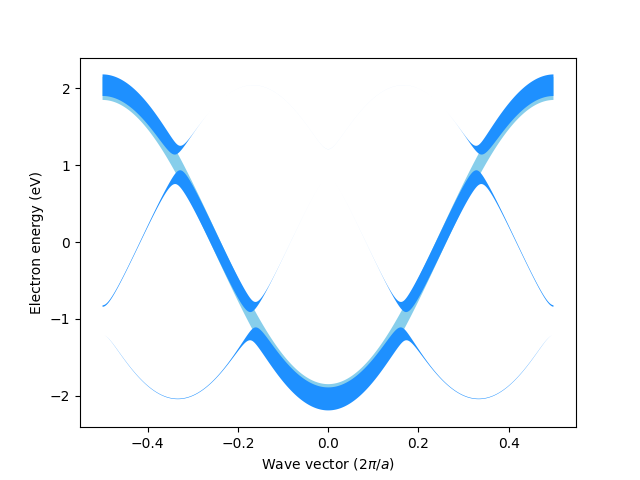
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Copyright (C) 2017-2026 elphmod Developers
# This program is free software under the terms of the GNU GPLv3 or later.
import elphmod
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
comm = elphmod.MPI.comm
t = 1.0 # hopping parameter (eV)
beta = -1.0 # scaling exponent
# atomic positions (lattice constant a = 1):
r = np.array([1.0, 2.0, 3.0]) # equidistant
R = np.array([1.1, 2.0, 2.9]) # trimerized
#R = r
nk = 1000 # number of k points
# Hamiltonian of equidistant chain:
def h(k1=0.0):
T = -np.array([
[t * np.exp(1j * k1)],
])
return T + T.transpose().conj()
# Hamiltonian of trimerized chain:
def H(k1=0.0):
t10 = t * ((R[1] - R[0]) % 3) ** beta
t21 = t * ((R[2] - R[1]) % 3) ** beta
t02 = t * ((R[0] - R[2]) % 3) ** beta
T = -np.array([
[0.0, 0.0, t02 * np.exp(1j * k1)],
[t10, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, t21, 0.0],
])
return T + T.transpose().conj()
# k-point sampling:
x = np.linspace(-0.5, +0.5, nk, endpoint=False)
k = 2 * np.pi * x
K = 3 * k
# calculation of band structure:
e, u = elphmod.dispersion.dispersion(h, k, vectors=True)
E, U = elphmod.dispersion.dispersion(H, K, vectors=True)
# weighting ("unfolding"):
w = np.ones(e.shape)
W = elphmod.dispersion.unfolding_weights(k, R, u, U, sgn=+1)
# plotting:
linewidth = 0.3
if comm.rank == 0:
for n in range(e.shape[1]):
fatband, = elphmod.plot.compline(x, e[:, n], linewidth * w[:, n])
plt.fill(*fatband, linewidth=0.0, color='skyblue')
for n in range(E.shape[1]):
fatband, = elphmod.plot.compline(x, E[:, n], linewidth * W[:, n])
plt.fill(*fatband, linewidth=0.0, color='dodgerblue')
plt.ylabel('Electron energy (eV)')
plt.xlabel(r'Wave vector ($2 \pi / a$)')
plt.savefig('peierls.png')
plt.show()